Stacking is a popular strategy in doubles pickleball. In this strategy, players switch positions during the game to optimize court coverage and play to their strengths. The goal is to position each player in the most effective spot, allowing them to handle shots more efficiently while hiding their weaknesses. For example, a right-handed and left-handed player on the same team can stack to maximize the effectiveness of their forehands and backhands.
After the serve, players often switch to new positions, one moving to the outside and the other staying closer to the center. This tactic helps create more offensive opportunities and exploit opponents’ weaknesses. While stacking can be powerful, it requires good communication and coordination, often through hand signals, to avoid confusion. Although it might seem tricky at first, with practice, stacking becomes a dynamic and effective tool for gaining an edge on the court.
Though it might seem like a weird strategy at first, once you understand the basics and get comfortable with the dimensions of the game, stacking becomes a dynamic tool to achieve more success on the court. However, players should also know the legal considerations to avoid violating rules.
Table of Contents
What is Stacking in Pickleball?
Stacking in doubles pickleball is a strategic positioning tactic used to improve court coverage and maximize each player’s strengths. The goal is to align teammates to minimize weaknesses and create a stronger offensive and defensive setup.
Typically, players switch places depending on whether they are serving or receiving, allowing them to position themselves based on their dominant hand—such as a right-handed player covering one side and a left-handed player covering the other. This setup increases the likelihood of successful shots and better coordination.
Players adjust their positions according to the score or game situation when using stacking. For example, teammates may split the court to optimize their attack depending on the first server’s position. The non-volley zone (NVZ) also plays a key role, as players must stay ready for volleys and manage shots from both sides.
While stacking can reduce unnecessary movement and increase consistency, it requires good communication and practice to avoid mistakes and ensure effective teamwork.
The Mechanics of Stacking in Pickleball
Stacking in pickleball involves players adjusting their positions on the court to maximize their strengths and improve overall team performance. Here’s how it works:
- Positioning Based on Strengths: Players move from the traditional court setup to one that better suits their skills. For example, a right-handed player might prefer the right side, while a left-handed player takes the left side to handle forehands or backhands better.
- Serving and Receiving Adjustments: Players position themselves according to their strengths. After each point, they switch places depending on who is serving or receiving, allowing for better court control.
- Maintaining Balance: The server might start on one side, and their partner aligns to cover the opposite side. As the game progresses, players shift along the sideline or to specific areas on the court to maintain strategic positioning.
- Quick Shifts: Players must be adaptable and move quickly between stacking positions to ensure they are ready to cover all shots, especially in the non-volley zone (NVZ).
Mastering stacking mechanics allows teams to exploit weaknesses in their opponents’ positioning, improving offense and defense.
Stacking on the Serve
Stacking on the serve in pickleball involves adjusting the players’ traditional court positions to maximize their strengths. Typically, players serve from the right side when the score is even and from the left side when it’s odd. However, with stacking, players may switch sides even during the serve to align with their preferred position, optimizing their shots.
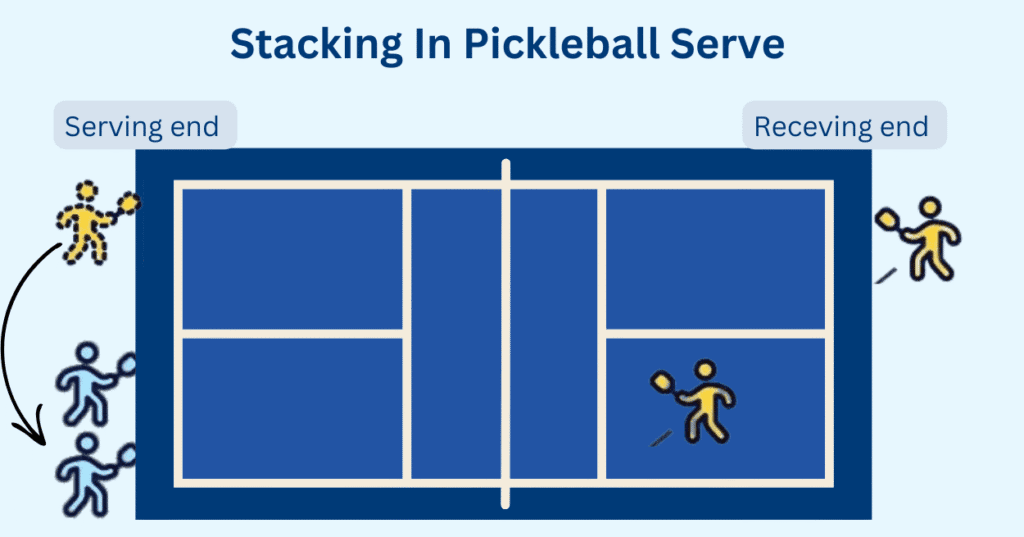
For example, if Player A is stronger on the left side and Player B prefers the right, they may stack by shifting positions before the serve, allowing both players to play to their strengths.
The server positions themselves without impeding play, while the non-serving partner may slide slightly to one side, ready to shift after the serve. This setup provides flexibility and quick adjustments, especially during crucial points. The non-volley line (NVZ) and net positioning are essential, as players must remain within the rules while executing the stack, giving them a strategic advantage.
Stacking When Returning a Serve
Stacking when returning a serve is a strategy that helps teams optimize their positions for a better advantage. Stacking allows players to align according to their preferred sides instead of staying in the traditional positions based on the score. For example, Player A may prefer the left, while Player B takes the right. This shift helps players prepare to hit more effectively from the baseline or near the non-volley zone (NVZ).
Effective stacking relies on flexibility and communication. Players use signals to transition between Full Stacking and Partial Stacking. After the return, the non-receiving partner may shift positions to avoid blocking each other. This strategy leads to smoother transitions, reduces confusion, and allows teammates to focus on their strengths. Stacking helps players return serves more efficiently and enhances teamwork for a more coordinated, fluid game.
Switching and Stacking in Pickleball
Switching and Stacking in Pickleball are complementary strategies to enhance team performance by exploiting strengths and outmaneuvering opponents. Switching involves players changing sides or positions during the game while stacking refers to players aligning in a specific formation to maximize coverage. During the serve and return, players shift positions to cover more ground and create strategic advantages.
For instance, after a serve, players might switch sides based on who is receiving, ensuring they are in their strongest position—whether it’s the left-hand or right-hand side. This allows the team to cover the court better and prevent the opponents from making easy shots.
Switch stacking is a fast-paced maneuver that requires clear communication to avoid confusion. With good coordination, players can cover more areas without disrupting play, making it harder for the opposition to predict the ball’s direction. The goal is to position players effectively, enabling them to hit their best shots while maintaining control.
How to Stack in Pickleball
Stacking is a strategy that optimizes player positioning to capitalize on each player’s strengths. The goal is to align players in positions that highlight their dominant skills while minimizing weaknesses.
For example, a stronger player might prefer the left side to hit forehand shots, while a less skilled player may be more comfortable on the right side, focusing on returns. This strategic alignment helps teams control the game, create better angles, and improve shot placement, much like how basketball teams use assists to set up plays.
However, if players aren’t well-coordinated, stacking can lead to confusion. Poor communication or sudden position shifts can disrupt the game, especially near the non-volley line. While stacking offers flexibility and more scoring chances, it requires smooth execution and timing. Teams must master the strategy to move seamlessly from serving to returning, ensuring they exploit the opponent’s weaknesses and maintain control of the court.
Using Hand Signals for Effective Stacking Communication
Using Hand Signals for Effective Stacking Communication in pickleball is essential for smooth coordination and strategy. Hand signals allow teams to communicate intentions discreetly without disrupting the game’s flow.
For example, a closed fist may signal to stay in the current position, while an open hand indicates a quick shift or role change. This nonverbal communication prevents confusion and breakdowns in coordination, reducing mistakes and missed opportunities.
Hand signals also help prevent the opposing team from anticipating moves. Subtle signals allow teams to catch their opponents off guard. Additionally, teams can use fake signals to mislead the opposition and gain an advantage.
In fast-paced situations, clear and quick signals ensure teammates can react swiftly without speaking, enhancing overall efficiency. Hand signals are crucial in executing a stacking strategy, helping teams stay ahead and maintain a competitive edge throughout the game.
Closed Fist in Pickleball Stacking
The closed fist is a common signal for players to communicate during a stacking strategy. When a player shows a closed fist, it typically indicates that they should stay in their current position on the court and maintain the initial setup. This signal is crucial for maintaining the team’s positioning without confusion.
For example, a player may use a closed fist to confirm that they are ready to continue the play from their side of the court, ensuring their partner knows no changes are required. This signal type helps teams be more efficient and coordinated, especially during fast-paced plays that require quick decisions.
Open Hand in Pickleball Stacking
The open hand signal plays a significant role in stacking, especially when a player intends to shift positions on the court. This signal typically signifies that the player plans to move to the opposite side or adjust their alignment for better coverage during the serve or return.
With an open hand, players can communicate their intentions clearly, helping to avoid miscommunication. This is especially important during high-stakes points, where precise positioning is crucial. The open hand signal ensures that all players are focused on the stacking process, allowing for a more efficient transition between positions and giving the team a strategic edge.
Is Stacking Legal in Pickleball?
Stacking in pickleball is a strategic positioning tactic many players use to gain an advantage during a serve or return. The good news is that stacking is legal as long as it follows the game’s basic rules. There are no specific restrictions or bans on the practice. Still, it must be done within the designated areas of the court, with the server and receiver starting in the correct positions before the rally begins.
According to rule 4.B.7. in the USA Pickleball Official Rulebook:
“In doubles, with the exception of the server (see 4.A.4) there is no restriction on the position of any player, as long as all players are on their respective team’s side of the net. They can be positioned on or off the court.”
If players shift or reposition during the serve, they can do so, but they must ensure that these moves do not violate the rules, such as stepping out of bounds or mispositioning themselves in a way that would cause a fault.
While stacking gives players the desired position for handling shots from either side, the server and receiver must follow the legal requirements for their side of the court. Miscommunication or incorrect positioning can result in faults or even lost points.
Stacking can still be used as a legitimate tactic in tournaments, where the rules are strictly enforced, but players must respect the legal guidelines to avoid penalties. As long as the players know the changes in position and initiate their shifts correctly, stacking remains a powerful, legal strategy to enhance the game.
Evaluating the Benefits and Drawbacks of Stacking
Pickleball has advantages and challenges. Stacking improves court coverage, as players are positioned based on their strengths. This allows for better shot execution and more aggressive play. It can also enhance a team’s ability to return difficult shots and pressure opponents.
On the downside, stacking requires precise execution. Poor communication or misalignment can disrupt the team’s flow, leaving them vulnerable to attacks. The strategy can be confusing if players don’t adjust quickly, particularly in high-pressure moments.
Additionally, constant position shifts may not suit every player’s style, affecting focus and performance. Despite these drawbacks, stacking remains a valuable tactic when executed with good coordination and clear communication, giving teams a strategic edge on the court.
Pros of Stacking in Pickleball
- Improves court coverage: Stacking helps players optimize their positioning, making covering more of the court easier.
- Better shot control: Allows players to control shots more effectively by positioning themselves where their strengths are most useful.
- Maximizes skills: It aligns players’ forehand and backhand preferences with the best position for each player, improving their performance based on their abilities.
- Reduces confusion: Stacking minimizes the need for switching and prevents confusion during play, making team movements more efficient.
- Creates a predictable setup: Teams can set up in a predictable pattern, ensuring everyone knows their role and where they are going.
- Minimizes errors: Stacking minimizes positional errors by ensuring players are comfortable, reducing chances for mistakes.
- Enables consistent offense: The strategy promotes a more consistent offensive play by placing players in positions that allow for better coverage of the non-volley zone and effective attacking angles.
- Increases team ability under pressure: Teams that use stacking are better able to handle pressure, making it harder for the opponent to disrupt their plays and positioning.
Cons of Stacking in Pickleball
- Complexity for beginners: Stacking can be challenging as executing properly requires high coordination and timing.
- Limits flexibility: Teams that rely too heavily on stacking may find it difficult to adjust to unexpected in-game scenarios, reducing their flexibility.
- Exploitable by opponents: If not executed well, stacking can leave gaps that opponents can exploit, leading to easy points.
- Increased physical demand: Maintaining a stacked formation can place physical demands on players, especially during frequent position shifts.
- Confuses partners: If communication breaks down or players are not accustomed to each other’s movements, stacking can confuse partners, leading to missteps.
- Potential for point losses: Mistakes in positioning or failure to maintain the stacked setup can result in costly point losses.
Optimizing Attacks with Stacking in Pickleball
Stacking is an incredibly useful strategy in doubles pickleball. It allows teams to cover the court more effectively and create offensive opportunities. Stacking enables players to use their strengths to the fullest by focusing on positioning and teamwork, ensuring they are in the best spots to handle returns and make powerful shots.
This strategy requires excellent coordination and often involves using hand signals to communicate where each player should be at any given moment, making it vital to stacking success.
Players must learn and practice stacking to improve their ability to hit better shots under pressure. With consistent practice, teams can gain an advantage over their opponents by using strategic shifts in positioning.
By coordinating their movements and capitalizing on each player’s strengths, stacking optimizes the team’s attacks and makes them more unpredictable. This ultimately boosts their chances of winning points and controlling the game.
Full Stacking
Full stacking is a strategy in which the team uses a full stack during both the serving and returning phases of the game, placing players in the most advantageous positions on the court. This technique aims to give the team the best chance to control the game by positioning players in alignment with their strengths.
While full stacking offers significant advantages, it can also be more complicated. The team must carefully track each player’s position to avoid confusion and disadvantageous shifts. If not executed properly, it can lead to costly mistakes, especially when players lose track of their position after a serve or during a return.
Partial Stacking
Partial stacking is a strategy where the team uses a stack during either the serving or returning phase but not both, allowing players to maintain their traditional positions during the other. This approach is often easier to track and manage since it doesn’t require constant repositioning like full stacking. It provides an advantage by allowing players to focus on their strengths while creating an opportunity to score.
However, partial stacking may place a player in a less-than-optimal position, giving the opponents a slight advantage, especially when facing strong serves. Although partial stacking can make serving easier and help the team rack up points, it may also leave players in a weaker position during certain game phases.
Half Stacking vs Full Stacking
Half-stacking and full-stacking are two variations of stacking strategies, each with strengths and challenges. Half-stacking is simpler and less complicated. It involves players using a stack only during the serving or receiving phase, not both. This allows players to prefer their traditional positions for part of the game, making managing it easier.
On the other hand, full stacking requires more coordination and communication as it involves the team stacking throughout both the serving and receiving phases. This can give players a stronger advantage by positioning them in their most effective spots for both offense and defense. Still, it can also be more difficult to execute and requires more focus, as players must constantly adjust their positioning.
The choice between half-stacking and full-stacking often depends on the players’ preferences and ability to coordinate as a team. Half-stacking is easier to implement, while full-stacking offers more potential for strategic control.
When to Stack in Pickleball
Knowing when to stack in pickleball makes the strategy valuable in your team’s arsenal. Stacking is most effective when it allows you to play to your teammate’s strengths and complement each other’s abilities, such as aligning forehands and backhands to cover the middle of the court.
It’s ideal to exploit an opponent’s weaknesses, like a weaker backhand or poor movement on one side. For example, if your teammate is left-handed and has a strong forehand, stacking can help position them to play to their strengths while you handle shots on the right side.
Stacking can also help mitigate situations when one player struggles or you must adapt quickly to an opponent’s attack. It helps maintain momentum by keeping your team in control of the center and allows you to react more effectively.
Mixing up your positioning can destabilize your opponents, keeping them guessing where you’ll be and making it harder for them to anticipate your next move. Stacking becomes a powerful tactic when understood and utilized correctly to reclaim the upper hand and stay ahead of your competition.
When Not to Stack in Pickleball
While stacking is an excellent strategy, it’s not always the best option, and in some cases, it can do more harm than good. Stacking has several downsides, especially if used constantly or without careful thought. Stacking can invite opponents to exploit weaknesses in your team’s positioning.
For example, if a right-handed player struggles with their backhand, stacking could force them to rely on it, negating their strengths and leaving them vulnerable. Stacking in such a situation could be limiting, putting players in positions that don’t suit their best forehand or shot.
Another issue arises when stacking puts a player in the center of the court, limiting their ability to cover other areas effectively. Stacking in these scenarios may create unnecessary risks, especially if players aren’t comfortable or stronger at defending the opposite side.
For less experienced or advanced players, stacking can result in errors without considering the fundamentals. Practice is key, but unless stacking complements each player’s abilities and strengths, it can cause more confusion than it’s worth. So, avoid stacking unless you’re confident it enhances your team’s reach and strategy.
Things to remember when staking
Create Time and Space
When stacking, it’s important to create time and space for your team to move effectively. This allows your players to switch positions smoothly during both the serve and return without consequences like missteps or positioning errors. Focus on executing returns with the right pace and arc, making it harder for your opponent to anticipate your next move.
Try to place the ball deep and directly across the court, forcing the opponent to move further away from their position while the server stays aligned to their designated line. This will give your team better game control and enhance your ability to cover the entire court.
Be Aware of the Gaps
Always be aware of the gaps in your team’s coverage when stacking. Opponents can quickly exploit any space or unguarded areas on the court, especially when players are moving around or shifting positions. A strong or hard shot into an open gap can easily break your defense.
To avoid this, ensure that your team maintains solid positioning and stays aware of any spaces that may become vulnerable during stacking. By closing these gaps and working together, you can reduce the risk of your opponents taking advantage of these openings.
Remember the Score
Always remember the score when stacking. Tracking the score helps your team stay ahead of your opponents and adjust your offensive and defensive strategies accordingly. Knowing whether you’re leading or trailing allows you to adapt your plan—whether to be more aggressive or play more conservatively.
By staying aware of the score, you can make smarter decisions about when to stack and shift and how to execute your next move to remain in control of the match.
Be Prepared to Stop
Be prepared to stop and adjust if needed during a stacking strategy. Avoid rushing to hit the ball while moving forward, as this can cause errors. If you need to stop, take a split step to ensure you’re in the correct position to react to the next shot.
Stopping briefly and resetting can help you continue with a more controlled and accurate movement, ensuring you’re always in the best spot to handle the next play. Being ready to stop and adjust prevents mistakes and keeps you in a strong position to defend or attack.
Tips for Playing Against Teams Who Are Stacking
- Ignore the stack: Focus on playing your game, and don’t get distracted by the stacking strategy.
- Catch them by surprise: Hit unexpected shots that force players to move quickly and disrupt their positions.
- Target the weaker side: Aim for the player’s backhand in the stack, especially if they struggle there.
- Keep the ball deep: Hit deep into the court to push the stack back and limit their movement options.
- Aim between players: Aim your shots between stacked players to create confusion and make it harder for them to cover the court.
- Be smart: Use your pickleball knowledge and experience to read the stacking team’s weaknesses and exploit them.
- Create confusion: Mixing up your shots and tactics can make it harder for them to stay coordinated.
- Don’t hesitate: Be quick to adjust and capitalize on any confusion or mistakes they make during stacking.
- Ask questions: If you’re unsure how they’ll respond, experiment with different shots or placements to test their weaknesses.
Why is stacking used in pickleball?
Stacking is used to:
Create a strategic advantage
Hide players’ weaknesses
Highlight the team’s strong side
Challenge opponents to hit the ball at specific angles or targets




Good – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a little bit, but other than that, this is fantastic blog. A great read. I will definitely be back.
Absolutely composed subject matter, Really enjoyed looking at.
I like this post, enjoyed this one appreciate it for putting up.
Howdy, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam remarks? If so how do you reduce it, any plugin or anything you can recommend? I get so much lately it’s driving me crazy so any support is very much appreciated.
doing manually
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen